Hospitals rely on hospital information systems (KIS) to digitize their processes. While these systems cover standard processes comprehensively, many individual processes must be mapped using master, control, reference, and parameter data – either individual tables or complex, interdependent table packages.
These catalogs are maintained by nursing professionals, most of whom lack technical knowledge. Since KIS does not include suitable, user-friendly, and auditable maintenance interfaces for catalogs, two unattractive alternatives arise:
For cost reasons, many institutions resort to a third, but error-prone option: data maintenance via MS Excel or MS Access, with manual transfer – without central data storage, logging, and audit compliance.
BOI FreeDa introduces a central platform on which all catalogs of a hospital or hospital operator can be edited securely and user-friendly — audit-proof, flexible, and without any programming effort.
Central data storage with multi-client capability
All catalog data is managed in one or more relational databases – BOI FreeDa acts as a single source of truth. Multi-client structures allow for the parallel maintenance of central and location-specific catalogs within one system.
User-friendly, audit-proof maintenance
Care professionals can edit their catalogs directly via the intuitive BOI FreeDa web interface without any database knowledge. Every change is seamlessly logged.
Mapping complex data dependencies
BOI FreeDa also enables the editing of highly networked catalogs through parent-child links – including validations and dependency checks during editing.
Customizable editing processes with verification mechanisms
Role system & access control
Only authorized employees can view and edit the catalogs that have been released for them. Access control and authorizations can be defined in great detail.
BOI FreeDa offers a ready-to-use, configurable solution for editing all KIS-catalogs, no matter how individualized, complex, or distributed the requirements are.
Advantages at a glance
Practical example
When BOI FreeDa was introduced, automatic checks detected 20 incorrect entries in a single KIS-catalog containing 87 lines. Additionally, 19 related entries were missing in referenced help tables — clear evidence of the added value of structured maintenance processes.
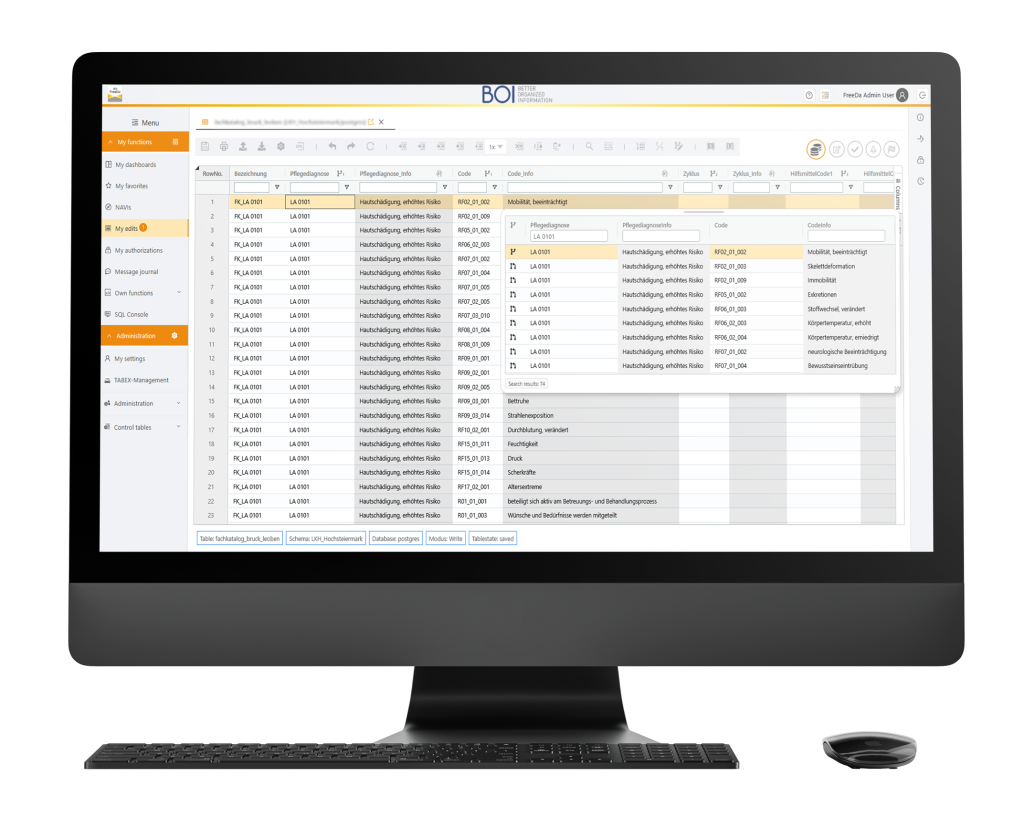
Within the BOI FreeDa system
Automatic Execution
Maintenance of simple catalogs: The interaction of medications or the delirium potential of medications is edited in one or more tables by several people in a role- and authorization- controlled, audit-proof manner. Roles, authorizations, and table processes are configured centrally by IT.
Maintenance of complex catalogs: The hospital operator is the central client and maintains the data in the various catalogs via BOI FreeDa. The care catalog consists of the „Diagnosis“ and „Variables“ catalogs as well as other catalogs. These define all possible diagnoses and their therapies, which make up the central care catalog.
Individual hospitals compile their own internal catalogs based on the central care catalog. Using BOI FreeDa’s RI Editor, hospitals can only use valid values from the central catalog. The 4-eyes control principle ensures that the hospital operator verifies the accuracy of the changes in the individual in-house catalogs. When changes are made to the central care catalog, all dependent in-house catalogs are changed and editing is required to ensure data consistency across all clients.
Feel free to contact us for a free, no-obligation consultation. We look forward to introducing you to our product. The data sent will be processed solely for the purpose of handling your request. For more details, please see our Privacy Policy.